What is Burn-in Testing in Electronics?
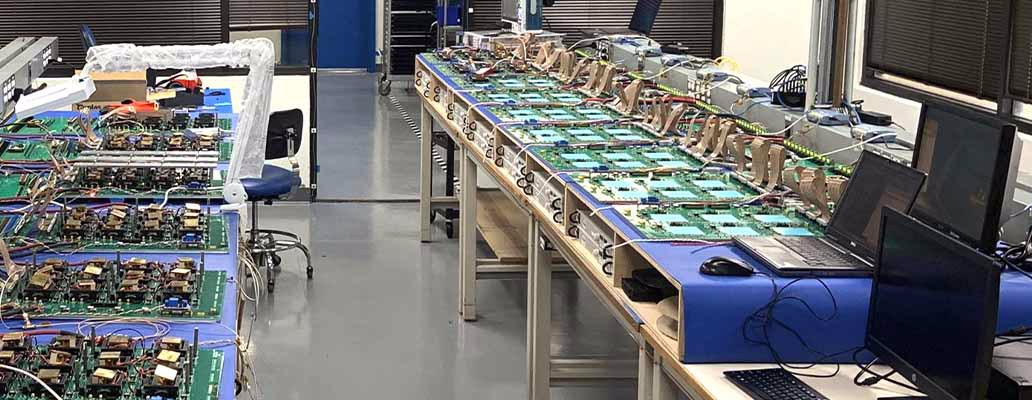
The process of Burn-in Testing is important in the field of electronics as it guarantees device reliability. It simulates real-world conditions to detect potential failures and address them early on. This ensures that products do not reach consumers with defects, such as malfunctioning smartphones or gaming consoles.
By serving as a quality checkpoint, burn-in testing greatly improves the reliability of electronic devices, making it an essential step in production. Familiarizing oneself with this process can provide valuable insights into the dependability of beloved gadgets and the careful measures taken during their manufacturing.
History of Burn-in Testing in Electronics
Burn-in testing originated in the early days of electronics to address component reliability issues. As technology advanced, manufacturers needed to ensure their devices were dependable, leading to the development of burn-in practices.
Initially used mainly in military and aerospace sectors, where reliability was crucial due to safety and mission-critical requirements, engineers sought methods to ensure components could endure harsh conditions over time.
With the rise of consumer electronics in the late 20th century, burn-in testing expanded to various devices, including televisions and computers. It became a standard practice in production lines worldwide, reflecting a commitment to product durability and quality control. This evolution highlights the importance of maintaining stringent standards to prevent unexpected failures and ensure long-lasting performance.
Why is Burn-in Testing Important?
In the electronics industry, burn-in testing is essential for several reasons:
- Early Failure Detection: It helps identify potential weaknesses in components by subjecting them to stress conditions, allowing manufacturers to uncover and address issues before products reach consumers.
- Enhanced Reliability: By filtering out defective units, burn-in testing ensures products meet customer expectations for flawless performance from day one.
- Cost Savings: Early detection of problems reduces warranty claims and maintenance costs, leading to long-term savings.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies that emphasize rigorous burn-in testing gain a competitive edge by delivering reliable products, building customer trust, and fostering loyalty.
As electronics become more complex, comprehensive burn-in testing remains crucial for ensuring consistent performance and high-quality standards.
How Does Burn-in Testing Work?
Burn-in testing involves exposing electronic components to elevated stress levels to accelerate their wear and reveal potential failures. This process typically includes subjecting devices to high voltage and temperature for extended periods, with engineers monitoring these conditions closely.
The test evaluates various parameters such as functionality, performance metrics, and thermal characteristics. Any irregularities detected can point to weaknesses in the design or manufacturing process.
To ensure higher reliability in final products, defects must be identified before they reach consumers. Burn-in testing simulates real-world usage scenarios in an accelerated timeline, providing insights into how well a device performs under typical operating conditions.
Types of Burn-in Tests
Burn-in testing includes various methods, each designed to ensure the reliability and performance of electronic components:
- Constant Voltage Burn-In Test: This method applies a steady voltage to devices and monitors their behavior over time. It helps identify early failures due to thermal or electrical stress.
- Temperature Cycling Burn-In Test: The test exposes devices to repeated cycles of high and low temperatures, simulating real-world conditions.
- Dynamic Burn-In Test: Devices operate under full capacity during this test, experiencing stressors similar to actual use cases. This approach evaluates performance under typical operational loads.
- Accelerated Life Testing (ALT): Devices are pushed beyond normal operating limits for shorter periods to expose latent defects more quickly than traditional methods.
Each type of burn-in test plays a crucial role in ensuring electronic devices meet high-quality standards before reaching consumers.
Benefits and Limitations of Burn-in Testing
- Early Failure Detection: Burn-in testing is an efficient method for pinpointing flaws in electronic components prior to their release into the market. It plays a critical role in catching issues that may not be detected through traditional testing techniques. Through the use of stress conditions like high temperatures and voltages, burn-in testing speeds up the aging process and exposes underlying defects that may otherwise surface at a later time. This proactive approach aids in avoiding defective products from ending up in the hands of consumers, resulting in a decrease in returns and warranty claims.
- Enhanced Reliability: By exposing products to stress conditions that simulate real-world usage over an accelerated time frame, burn-in testing enhances the overall reliability and durability of electronic devices. This strict testing ensures that components are not only functional but also robust enough to withstand everyday wear and tear. As a result, products are less likely to fail prematurely, fostering customer trust and increasing brand loyalty.
Limitations of Burn-in Testing
- Cost and Time: Burn-in testing can be both costly and time-consuming. The process requires specialized equipment and facilities to maintain the necessary stress conditions, as well as skilled personnel to monitor and analyze the results. Additionally, the testing period can vary from several hours to days or even weeks, depending on the complexity of the product and the testing standards required. For smaller manufacturers with limited resources, these costs and time commitments can be a significant burden, potentially affecting their ability to compete with larger companies that have more extensive testing capabilities.
- Limited Scope: Burn-in testing effectively detects early-life failures but has limitations in predicting long-term performance issues or defects that may arise later. It mainly addresses initial “infant mortality” failures and may not account for problems from extended use, environmental conditions, or material fatigue, thus not guaranteeing flawless performance throughout the product’s lifespan.
Balancing these benefits and limitations is essential for manufacturers to maintain high quality while staying competitive in the rapidly evolving electronics market.
Common Misconceptions About Burn-in Testing
Here are some common misconceptions about burn-in testing:
- Just for Identifying Defects: Many people think burn-in testing is solely about spotting defective components. In reality, its primary purpose is to ensure overall product reliability by simulating stress conditions. This helps in identifying potential weaknesses that could affect the product’s performance over time, not just immediate defects.
- Only for Consumer Electronics: Some believe burn-in testing is only relevant for consumer electronics. However, it is crucial in various industries, including aerospace, medical devices, and military applications, where reliability is vital due to potential serious consequences. In these fields, ensuring that components can endure extreme conditions and long-term use is critical.
- Guarantees Longevity: There’s a misconception that burn-in testing guarantees a product’s long-term durability. While it is effective at detecting early-life failures, it does not predict how a product will perform under all possible future conditions. Burn-in testing focuses on identifying issues that occur soon after manufacturing but may not reveal all long-term performance problems.
- Excessively Time-Consuming: Some think burn-in testing takes too long. Advances in technology have made burn-in testing more efficient, reducing the time required while still providing valuable results. Modern techniques and improved testing environments have streamlined the process, allowing for effective testing without excessive delays.
- Outdated or Unnecessary: A common belief is that burn-in testing is outdated or unnecessary with modern manufacturing advances. Contrary to this belief, burn-in testing remains a vital part of quality assurance. It helps maintain high standards by ensuring products meet reliability and performance criteria, which is important in a competitive market where quality cannot be compromised.